Osteoporosis Treatment
Comprehensive Osteoporosis Treatment
For Improved Bone Health
Osteoporosis treatment is a progressive bone condition wherein there is a loss of bone mass, which leads to a decrease in bone strength. They become brittle, weak and more susceptible to fracture. The bones undergo change throughout life. Up to the age of 30, bone is made, and very little is broken down. After the age of 30, it is broken down faster. This loss is further aggravated after menopause. So if you think you may have weak/brittle bones, do not wait for a fracture to happen. Seek an appointment with Dr. Kaishreen for a full assessment of your bone health.
Osteoporosis is a progressive bone disease characterized by reduced bone density and increased fragility, leading to a higher risk of fractures. Effective treatment for osteoporosis typically involves a multifaceted approach aimed at slowing bone loss, improving bone density, and minimizing fracture risk. One primary treatment modality is pharmacotherapy, which includes bisphosphonates such as alendronate and risedronate.
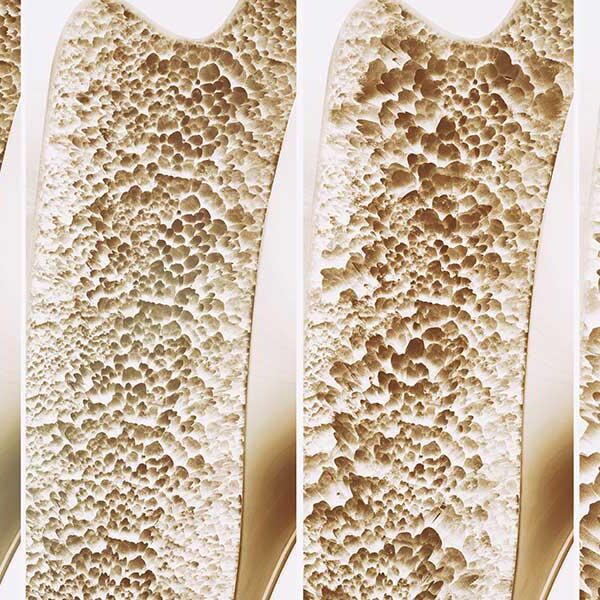
These drugs work by inhibiting bone resorption, thus slowing the rate of bone loss. Other medications like selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) and hormone replacement therapy (HRT) can also play a role, especially in postmenopausal women, by mimicking estrogen’s protective effects on bones. Additionally, newer treatments such as denosumab, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits osteoclast activity, and teriparatide, a parathyroid hormone analog that stimulates new bone formation, are used for more severe cases.
In conjunction with medication, lifestyle modifications are crucial for managing osteoporosis. Weight-bearing and resistance exercises are recommended to strengthen bones and muscles, thereby reducing the risk of falls and fractures. Nutrition also plays a key role; a diet rich in calcium and vitamin D is essential for maintaining bone health. Calcium can be sourced from dairy products, leafy green vegetables, and fortified foods, while vitamin D, which aids in calcium absorption, can be obtained through sunlight exposure and dietary supplements. Smoking cessation and limiting alcohol intake are also important, as both smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can negatively impact bone density.
Regular monitoring and assessment are essential for individuals undergoing osteoporosis treatment. Routine bone density tests, such as dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA), help evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment and guide any necessary adjustments. Patient education on fall prevention strategies is also vital; simple changes like installing grab bars in the bathroom and ensuring adequate lighting can significantly reduce the risk of falls. Collaboration between healthcare providers, patients, and caregivers ensures a comprehensive treatment plan, addressing both medical and lifestyle factors to manage osteoporosis effectively and improve quality of life.
